Two models of communication
1. Linear model of communication
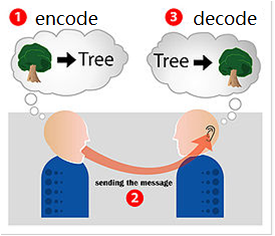
2. Circular model of communication
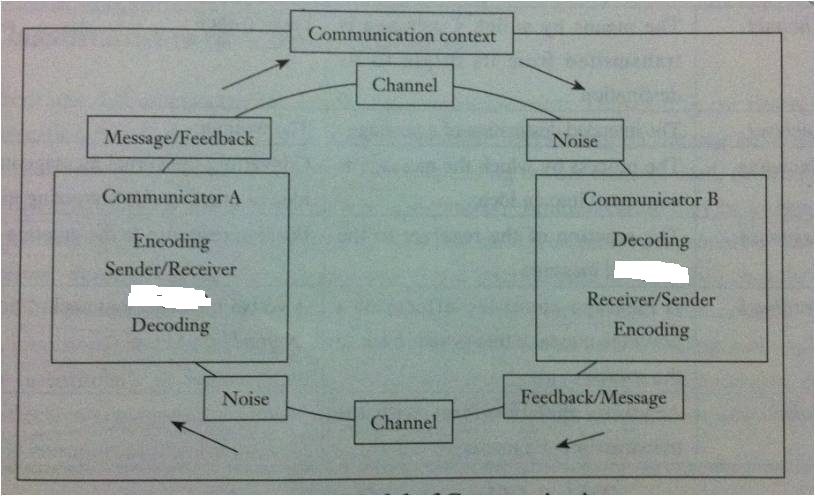
Elements of communication (textbook p. 41)
sender/source: the person who transmits a message
message: any signal that triggers the response of a receiver
encoding: the activity during which the sender must choose certain words or nonverbal methods to send an intentional message
channel: the method to deliver a message
receiver: any person who notices and gives some meaning to a message
decoding: the activity during which the receiver attaches meaning to the words or symbols
feedback: the response of a receiver to a sender's message
noise: factors that interfere with the exchange of messages, including external noise, physiological noise, psychological noise and semantic noise
external noise: e.g. voice in the next room, ring of cell phone
physiological noise: e.g. illness and disabilities make people difficult to send or receive a message.
psychological noise: e.g. hostility, preoccupation
semantic noise: e.g jargon or technical terms which are not understood by the listener
context: the setting or situation in which the communication occurs


