Text A & B Significance, definition and functions
1. Significance (Textbook p. 170)
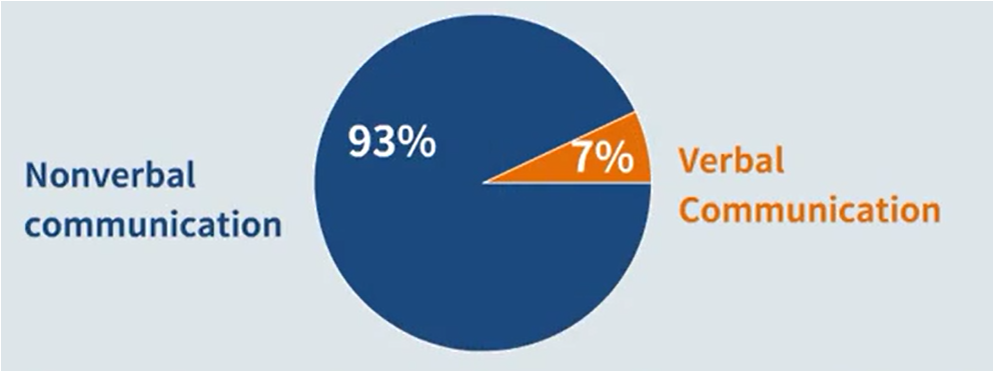
(1) nonverbal communication encompasses 93% of the meaning in communication.
(2) nonverbal behaviors spontaneously reflects the subconsciousness.
e.g. accomplished liars can be detected by subtle nonverbal cues they unknowingly give
(3) nonverbal communication is significant is that we cannot avoid communicating
e.g. even silence conveys meaning too
2. Definition of nonverbal communication
Nonverbal communication: the messages sent without words. (Textbook p. 172)
3. Functions of nonverbal communication
(1) repeating
e.g. say "Let's be quiet" and place the finger to the lips
(2) complementing
e.g. smile and say "How are you!"
(3) substituting
e.g. a small child points to the toy in stead of saying " I want it".
(4) regulating
e.g. turn-taking signals in conversations to indicate the speaker has finished talking
(5) contradicting
e.g. shrink back and frown while say " I love you".


